IOT Development & Integration
IoT (Internet of Things) development and integration with RFID and NFC technology can significantly enhance the capabilities of web and mobile applications, enabling seamless communication between physical objects and digital systems. Let’s explore the key aspects of IoT development and how RFID and NFC integration can be leveraged in web and mobile apps:
1. IoT Development:
- Device Integration: IoT development involves connecting physical devices, sensors, and actuators to the internet or a local network, enabling them to communicate and exchange data.
- Data Collection: IoT devices collect data from the environment they monitor, such as temperature, humidity, motion, or other relevant parameters.
- Data Transmission: IoT devices transmit the collected data to a central server or cloud-based platform for further processing and analysis.
- Remote Control: Depending on the application, IoT devices can also receive commands from the server to perform specific actions.
2. RFID and NFC Integration:
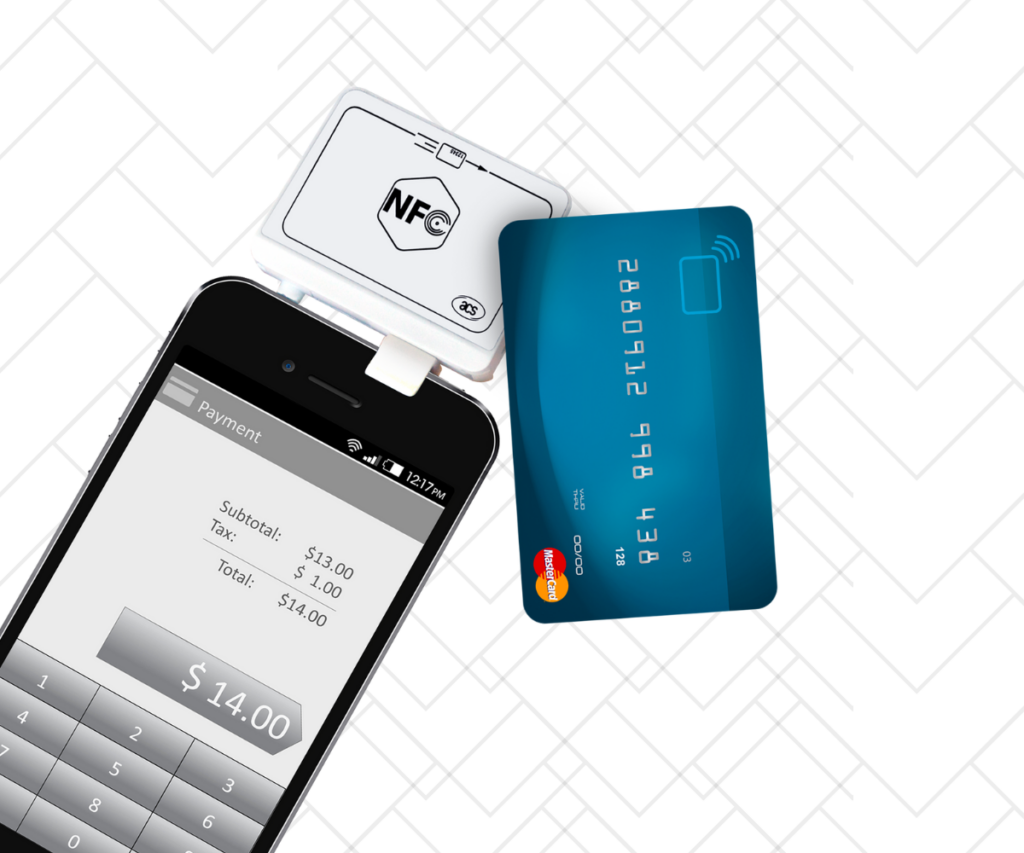
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): RFID uses radio waves to identify and track objects equipped with RFID tags. These tags contain unique identifiers that can be read by RFID readers.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): NFC is a subset of RFID technology that allows devices to communicate when they are in close proximity (within a few centimeters).
- Use Cases: RFID and NFC integration can be used for inventory tracking, access control, contactless payments, authentication, and more.
3. Integration with Web and Mobile Apps:
- Data Visualization: Web and mobile apps can display real-time data collected from IoT devices, providing users with insights into the monitored environment.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Apps can enable users to remotely monitor and control IoT devices, adjusting settings or receiving alerts based on data received from the devices.
- User Authentication: RFID or NFC can be integrated into the app for secure user authentication or access control, allowing users to log in or access specific areas using their RFID/NFC-enabled devices.
- Location-Based Services: NFC can facilitate location-based services, allowing users to interact with physical objects or receive information based on their proximity to NFC tags or readers.
4. Security Considerations:
- Secure Communication: Implement secure communication protocols between IoT devices and the web/mobile app to protect data integrity and privacy.
- Authentication and Authorization: Ensure that only authorized users or devices can access and control IoT devices through the app.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data transmitted between IoT devices and the app to prevent unauthorized access.
5. Scalability and Performance:
- Ensure that the IoT infrastructure and app architecture can scale to handle a large number of connected devices and concurrent users.
- Optimize data processing and storage to maintain app performance and responsiveness.
By integrating RFID and NFC technology with web and mobile apps in IoT development, businesses can unlock new possibilities for automation, data collection, and user interactions. The seamless communication between physical objects and digital systems brings efficiency, convenience, and enhanced user experiences to various industries and use cases.